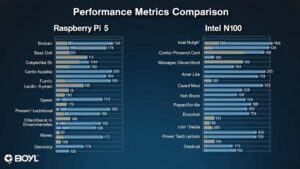
When you compare the Raspberry Pi 5 vs Intel N100, you’ll notice distinct performance metrics. The N100 outperforms the Pi 5 in CPU benchmarks and multi-core tasks, thanks to its higher clock speeds and cache. While the Pi 5 excels in energy efficiency, its lower power consumption makes it ideal for battery-powered projects. Regarding graphics, the N100’s integrated graphics greatly surpass the Pi 5. Additionally, N100 supports more memory options, enhancing multi-threaded performance. However, the Pi 5 shines in lower-cost applications. To grasp the full scope of their capabilities, you might explore further details.
Key Takeaways
- Intel N100 outperforms Raspberry Pi 5 in multi-core benchmarks, achieving a Sysbench score of 44,058 compared to Pi 5’s 40,359.
- The N100 has superior single-core performance, scoring 1934 in Geekbench, while Raspberry Pi 5 scores only 752.
- Raspberry Pi 5 is more energy-efficient, consuming 3-4W idle and up to 9W under load, compared to N100’s 22-27W.
- N100 supports up to 16 GB of DDR4/DDR5 memory, whereas Raspberry Pi 5 is limited to 8 GB of LPDDR4X RAM.
- In graphics performance, N100’s integrated GPU scores 2070 in GLMark2, greatly surpassing Raspberry Pi 5’s score of 307.
Processor Architecture Comparison
When comparing the processor architectures of the Raspberry Pi 5 and Intel N100, you’ll notice distinct differences that greatly impact performance.
The Raspberry Pi 5 boasts a Broadcom BCM2712 SOC, featuring a 4-core Arm A76 processor capable of clock speeds up to 2.4 GHz. It utilizes the ARMv8 architecture, which emphasizes energy efficiency, but lacks any turbo boost functionality, placing constraints on its peak performance capability.
In contrast, the Intel N100 leverages Gracemont cores from the Alder Lake-N series, reaching clock speeds up to 3.4 GHz with turbo boost. This architecture design provides flexibility, allowing it to adjust performance based on workload demands. N100 PC consumes additional power, typically almost four times that of the Pi 5, which can impact energy costs. Notably, the N100 supports DDR4-3200 or DDR5-4800, providing enhanced memory configurations that benefit performance in demanding tasks.
Additionally, the N100 comes with 6MB of L3 cache, further enhancing its processing capabilities.
These architecture differences are significant when evaluating tasks requiring varying degrees of processing power. While the Raspberry Pi 5 is optimized for energy-efficiency applications, the Intel N100 is designed for more demanding environments, supporting higher clock speeds and upscale memory configurations.
Ultimately, your choice hinges on the intended application, whether it’s compact designs or higher-performance needs.
CPU Benchmark Performance
When comparing the CPU benchmark performance of the Raspberry Pi 5 and Intel N100, you’ll notice distinct differences in multi-core and single-core performance. The thermal limitations of the Raspberry Pi 5 could impact its efficiency under heavy loads, affecting overall scores. Notably, the N100 averages 9% faster in the Sysbench CPU benchmark than the Pi 5. Additionally, the Pi 5 has demonstrated significant performance gains across its benchmarks when compared to its predecessor, the Pi 4. Analyzing these factors will give you a clearer picture of how each system performs in real-world applications.
Multi-Core Performance Comparison
Evaluating the multi-core performance of the Raspberry Pi 5 and Intel N100 reveals considerable differences in their CPU benchmark outcomes. Here are three key takeaways:
- Sysbench Scores: The Intel N100 averages at 44,058, while the Raspberry Pi 5 trails slightly behind at 40,359.
- Geekbench Multi-Core Scores: The Pi 5 scores 1617, reflecting a 219.1% improvement over the Pi 4.
- Thermal Management: N100 displays more consistency in performance, indicating better thermal control compared to the Pi 5. Additionally, the Raspberry Pi 5 excels in single-core performance, which might influence its overall versatility in various tasks. Its higher memory capacity compared to the Raspberry Pi 4 also aids in handling multiple applications simultaneously.
When evaluating multi-core optimization, both systems exhibit efficient threading, but the N100’s higher clock speeds contribute to its superior performance despite similar core counts.
The Raspberry Pi 5’s architecture provides excellent power efficiency, making it ideal for battery-powered applications.
However, during intensive tasks, an active cooler can greatly aid its sustained throughput, highlighting the importance of thermal management in CPU performance.
Single-Core Performance Insights
The single-core performance of the Raspberry Pi 5 and Intel N100 highlights considerable variances that shape their usability in different applications. When considering single thread efficiency, these differences primarily arise from distinct architectural choices and clock speeds.
| Metric | Raspberry Pi 5 | Intel N100 |
|---|---|---|
| Base Clock Speed | 2.4 GHz | 0.7 GHz |
| Turbo Clock Speed | N/A | 3.4 GHz |
| Single-Core Geekbench Score | 752 | 1934 |
| L1 Cache Size | 64 KB | 64 KB |
| L3 Cache Size | 2 MB | 6 MB |
The Intel N100 outperforms the Raspberry Pi 5 in single-core benchmarks, achieving superior scores in PassMark software. This directly impacts workload optimization, making the Intel N100 better suited for tasks requiring high single-thread performance. While the Raspberry Pi 5 shows substantial advancements over its predecessor, its score notably lags behind that of the N100. Ultimately, the decision comes down to what you need—if single-core tasks are your focus, the N100 excels in efficiency, while the Raspberry Pi 5 may still shine in specific applications requiring robust multi-threading capabilities. Additionally, the Intel N100 shows 18% higher performance in multi-threaded testing, which can also influence overall user experience depending on the workloads involved. Furthermore, the Intel N100 features a larger L3 cache size compared to the Raspberry Pi 5, which can further enhance its performance in demanding applications.
Thermal Limitation Effects
While both the Raspberry Pi 5 and Intel N100 face thermal limitations, their impacts on CPU benchmark performance vary markedly. Understanding these differences can help optimize your projects.
- Raspberry Pi 5 peaks at 86.7°C, triggering thermal throttling and leading to performance declines.
- Intel N100 reacts differently, throttling at around 64°C, but remains below 48°C with effective cooling solutions.
- Active cooling is vital; the Raspberry Pi 5 can stabilize performance when paired with proper cooling solutions, like active coolers reducing temperatures to around 59°C. Additionally, the designed GPIO pins on the Raspberry Pi 5 allow for enhanced compatibility with cooling solutions. Moreover, during stress testing, notable temperature drops were observed, underscoring the effectiveness of thermal management strategies.
For the Raspberry Pi 5, without cooling, power consumption increases considerably under stress, from 2.7 Watts at idle to 7 Watts. This raises the risk of thermal throttling affecting performance during sustained workloads.
On the other hand, the Intel N100, while it can also throttle, benefits greatly from adjustable BIOS settings and modifications, such as copper shims, to enhance cooling.
Ultimately, employing robust cooling solutions is essential for both devices. Ensuring stable operation and responsiveness can drastically improve the overall user experience.
Memory Capacity and Speed
Memory capacity and speed play critical roles in determining the performance of devices like the Raspberry Pi 5 and Intel N100. The Raspberry Pi 5 maxes out at 8 GB of LPDDR4X-4267 SDRAM, while the Intel N100 supports up to 16 GB with options for DDR4 and DDR5, reaching speeds of up to 4800 MT/s. This difference in capacity and speed highlights the potential for performance tuning, particularly in multi-threaded environments where higher memory bandwidth is essential. Additionally, the Intel N100 features Intel Speed Shift Technology, which optimizes power efficiency and performance further, making it a strong contender in its class.
You’ll notice that the Raspberry Pi is available in varied RAM sizes, which can impact performance depending on your tasks. As you’ve probably found, systems with lower RAM can bottleneck when handling heavier workloads. The importance of power efficiency in these systems cannot be overstated, especially for long-term usage. Additionally, the Raspberry Pi 5 has a maximum purchase limit of 10 units per customer, underscoring its popularity among developers and enthusiasts alike.
For the N100, while it only has a single memory channel, its support for faster RAM types could mitigate this limitation. When considering memory upgrade strategies, the Intel N100 presents more flexibility. It proves advantageous in resource-intensive applications. Ultimately, both platforms serve unique purposes, but if speed and capacity matter considerably to your projects, the Intel N100 takes the lead in this comparison.
Storage Speed and Efficiency
When evaluating storage speed and efficiency, you’ll notice significant differences between the Raspberry Pi 5 and Intel N100.
The Raspberry Pi 5 boasts impressive sequential read speeds up to 800MBps and write speeds reaching 450MBps, thanks to its NVMe capabilities. In addition, its memory read/write speeds of 85MB/s—almost double that of Raspberry Pi 4—further enhance its data handling performance.
In contrast, while the Intel N100 can theoretically achieve higher rates, its single-channel configuration limits real-world performance, especially in demanding tasks. Furthermore, the Intel N100 features a 2242 M.2 NVMe slot that offers competitive storage flexibility.
Sequential Read Performance
In comparing the sequential read performance of the Raspberry Pi 5 and Intel N100, it’s clear that storage speed and efficiency greatly impact overall system capabilities. The differences in their performance metrics reveal vital insights into their usability:
- Raspberry Pi 5: Averages around 423 MB/s in sequential reads, limited by its single PCIe lane. This limitation is similar to other mini PCs that rely on single PCIe lanes for data transfer.
- Intel N100: Reaches about 673 MB/s, benefiting from dual PCIe lanes for superior bandwidth.
- Benchmark Scores: The Pi 5 scores 32,089, while the N100 boasts a considerably higher score of 44,803.
The Raspberry Pi 5 shows improvements over its predecessor, yet its read speeds pale in comparison to the N100’s. This performance gap illustrates the N100’s higher RAM support, allowing it to handle more intensive applications efficiently.
The dual PCIe lanes of the N100 facilitate faster data access, enhancing overall system responsiveness. This key advantage makes the Intel N100 particularly suited for high-bandwidth tasks. Additionally, the N100 operates at a higher clock speed of up to 3.4 GHz, which further contributes to its performance in various scenarios. The N100’s ability to handle demanding tasks is also enhanced by its robust cooling system, which is essential for maintaining performance under load.
While the Pi 5’s SSD configuration offers an upgrade from microSD cards, it still can’t match the N100’s consistent performance across various tests.
When evaluating your options, these sequential read speeds should play a notable role in your decision-making process for performance-driven tasks. Considering factors such as external GPU options can also help in making an informed choice about which mini PC best suits your needs.
Write Speed Comparison
How do the write speeds of the Raspberry Pi 5 compare to those of the Intel N100? The differences are stark. The Pi 5 averages a write speed of 241 MB/s, while the Intel N100 nearly doubles this with 495 MB/s. This disparity stems largely from write speed factors like the storage configuration.
The N100 utilizes two PCIe lanes, enhancing its efficiency and overall performance. In contrast, the single PCIe lane on the Raspberry Pi 5 can become a bottleneck, particularly when connecting multiple drives. Consequently, the Intel N100’s architecture supports better storage scalability and efficiency. Additionally, the AMD64 architecture of the N100 allows compatibility with more advanced operating systems, which can further optimize its performance.
In terms of performance implications, you’ll notice the N100 exhibits consistent write speeds critical for demanding applications. Its additional SATA port also provides flexibility, accommodating more storage devices without sacrificing performance. This is particularly beneficial due to the energy efficiency of SSDs, which extends battery life and reduces heat generation.
Meanwhile, the Pi 5 is limited in this scope, hampered by its design. Overall, if you prioritize write speed and efficiency in your computing needs, the Intel N100 stands out as the superior choice, proving more adept at handling intensive tasks while maintaining stable performance across benchmarks.
Graphics Processing Capabilities

You might be surprised by the differences in graphics processing capabilities between the Raspberry Pi 5 and Intel N100. A detailed graphics performance evaluation reveals some striking contrasts:
- GPU Models: Raspberry Pi 5 uses the Broadcom VideoCore VII GPU, while the Intel N100 features 24EU Intel HD graphics.
- Benchmark Scores: In the GLMark2 benchmark, the Raspberry Pi 5 scores 307, whereas the Intel N100 boasts a score of 2070, making it over 6.5 times faster.
- Video Playback: The Raspberry Pi 5 struggles with 1080P video, experiencing stutters, while the Intel N100 delivers smooth playback. Additionally, the Raspberry Pi 5’s advanced camera capabilities underscore its ability to handle specific multimedia tasks, albeit in a limited capacity. The improved performance of the Raspberry Pi 5 can be attributed to its Broadcom VideoCore VII GPU, enhancing its graphics capabilities in general tasks. This is similar to how the Mac Mini 2024’s compact design enhances its versatility in various environments.
This GPU architecture analysis shows that while the Raspberry Pi 5 handles basic graphics tasks adequately, it has limitations in more demanding applications, such as video editing.
The Intel N100, on the other hand, excels in graphics-intensive tasks and supports more advanced graphics APIs, including DirectX 12.1 and OpenGL 4.6. It also benefits from extensive connectivity options like those found in the Mac Mini 2024, such as Thunderbolt ports.
If you’re looking for robust graphics capabilities, the Intel N100 clearly outperforms the Raspberry Pi 5, which may better suit casual users focused on lightweight applications.
Power Consumption Analysis
When considering performance in graphics, it’s also important to evaluate power consumption, especially if you’re looking for a device that fits within specific energy constraints.
The Raspberry Pi 5 stands out with an idle power consumption of just 3-4W, while the Intel N100 typically operates around 8W at idle. With optimizations, the N100 can lower its idle efficiency to as low as 1.3-1.5W, but real-world usage often sees higher figures, sometimes up to 10W.
Under load, this disparity widens markedly. The Raspberry Pi 5 consumes 8-9W, remaining relatively stable, while the N100 can demand up to 27W, even settling around 22-23W in optimized scenarios. Additionally, the N100’s maximum power consumption peaking at 22-23W can significantly impact energy efficiency in high-performance tasks.
This increased load performance not only impacts operational costs but also influences the viability of battery-powered applications.
For power-sensitive setups, the Pi 5’s efficiency makes it a clear winner. ARM architecture is inherently more power-efficient, translating to longer battery life for portable applications.
On the other hand, for mains-powered projects, while the power difference may seem less critical, the cumulative savings from the Pi 5’s lower consumption shouldn’t be underestimated.
Operating System Versatility
When considering the Raspberry Pi 5, you’ll notice that its supported operating systems play a vital role in optimizing performance.
With options like the official Raspberry Pi OS, Ubuntu, and Armbian, you can tailor your setup based on your needs, but remember to stay updated for compatibility.
As you weigh these choices, it’s also essential to assess the security features each OS offers to safeguard your projects.
Supported Operating Systems
Operating system versatility plays an essential role in determining the overall functionality of computing devices like the Raspberry Pi 5 and Intel N100. Here’s a quick comparison of their supported operating systems:
- Raspberry Pi 5 offers a range of options like Raspberry Pi OS, Ubuntu, and specialized distributions tailored for media or retro gaming. The open-source nature of these distributions allows for extensive modification and distribution.
- Intel N100 effortlessly runs various operating systems, including Windows and multiple Linux distributions, thanks to its x86 architecture. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for users who require broad software compatibility.
- Community support for both platforms enhances user experience by providing additional OS options and troubleshooting resources.
While the Raspberry Pi primarily supports ARM-compatible systems, the flexibility of the Intel N100 allows for a broader selection.
The installation process also differs; Raspberry Pi Imager simplifies getting started, whereas the Intel N100 requires downloads from respective websites, reflecting its versatile OS compatibility.
Despite having fewer options, the Raspberry Pi benefits from robust community-backed support.
Ultimately, if you value system efficiency and variety in software flexibility, the Intel N100 delivers a superior OS experience, whereas the Raspberry Pi offers a streamlined yet effective multi-OS environment.
Additionally, users considering Chrome OS on these devices should note its automatic updates ensure system security and functionality without manual intervention. This is similar to how Linux distributions can run on less powerful hardware, enhancing accessibility.
Security Features Comparison
A thorough analysis of security features reveals notable differences between the Raspberry Pi 5 and Intel N100. The Raspberry Pi 5 incorporates a robust secure boot mechanism that guarantees only authenticated software runs, leveraging a SHA256 hash stored in One-Time Programmable (OTP) memory to deter key tampering. This advanced boot system effectively guards against malware and viruses, ensuring that only trusted software is executed during the boot process.
In contrast, the Intel N100 lacks an intrinsic secure boot process and instead uses UEFI firmware, which can be configured for secure boot, but doesn’t provide the same level of integration as the Raspberry Pi 5’s solution.
When it comes to hardware encryption, the Raspberry Pi 5 excels by offering dedicated hardware encryption that secures data and communications without significant performance overhead. On the other hand, the Intel N100 must rely on software-based encryption, which can hamper performance.
User authentication on the Raspberry Pi 5 allows you to disable the default user account and create a custom one, enhancing security and access control. The Intel N100 manages user authentication through the OS, often requiring additional interventions for peak security.
Thermal Management Considerations

Thermal management plays an essential role in maximizing the performance of both the Raspberry Pi 5 and Intel N100, especially during intensive tasks.
Implementing effective thermal management strategies is vital to avoid thermal throttling, which can greatly hinder processing speeds. Effective thermal management is also crucial for maintaining the overall longevity of the system, similar to how community support helps in troubleshooting and optimizing Linux installations.
Here are three key performance optimization techniques for consideration:
- Active Cooling Solutions: The Raspberry Pi 5’s Active Cooler employs an anodized aluminum heatsink and an integrated fan, activating at 60°C to maintain an ideal temperature range of 60-63°C under load.
- Throttling Awareness: Knowing that the Raspberry Pi 5 begins to throttle at 80°C allows you to monitor and plan workload intensity to prevent performance drops during critical tasks.
- Passive Cooling Limitations: While passive cooling may suffice at idle, under heavy loads, it can lead to increased temperatures and throttling, making it less effective than an active cooling system.
Application Use Cases
When it comes to application use cases, both the Raspberry Pi 5 and Intel N100 excel in different scenarios, making them suited for distinct user needs.
The Raspberry Pi 5 shines in home automation, serving as an effective smart home hub that integrates with various smart devices using protocols like Zigbee or Z-Wave. Its capabilities extend to environmental monitoring, allowing you to automate tasks based on humidity or weather data.
For media streaming and gaming performance, the Raspberry Pi 5 is versatile enough to function as a home media center with Kodi and even handle real-time gaming tasks, albeit with less graphical power than the Intel N100. The latter excels in demanding gaming and media tasks with superior GPU capabilities. For instance, if you’re looking to set up a Plex server for media streaming, the Intel N100’s robust specs are more aligned with Plex server requirements for optimal performance.
In the domain of learning development, the Raspberry Pi 5 is a fantastic platform for those diving into Arm-based systems and robotics projects, thanks to its GPIO operations.
For edge computing, its ability to process data locally is a significant asset, reducing latency in smart applications.
Ultimately, your choice will depend on your specific needs and desired innovations in home automation, entertainment, or development.
Price-to-Performance Ratio
In comparing the price-to-performance ratio of the Raspberry Pi 5 and Intel N100, it’s clear that each offers distinct advantages based on user needs.
When you’re evaluating which option fits your project best, consider the following:
- Cost Effectiveness: The Raspberry Pi 5 is budget-friendly at approximately $126, but lacks included components like an enclosure.
- Performance Metrics: While the N100 costs similarly, it outperforms the Pi 5 in CPU, GPU, and storage benchmarks, providing more value regarding performance per dollar. For example, mini PCs like the Beelink S12 Pro with the Intel N100 processor offer efficient multitasking.
- Upgrade Potential: The N100 offers M.2 ports and additional PCIe lanes for future upgrades, making it a more flexible solution.
Your cost effectiveness analysis should factor in not just the initial cost but also the performance gains and potential for future enhancements.
If power efficiency is a priority, the Raspberry Pi 5 shines as a low-power alternative, ideal for battery-powered applications.
However, if raw performance and integration into a broader software ecosystem are essential, the Intel N100 stands as a compelling option that justifies its value in performance-intensive tasks. This is particularly relevant when considering devices designed for everyday computing and media consumption, such as the KOOSMILE Mini PC.
Ultimately, your final choice hinges on the specific needs of your projects.
Considering mini PCs under $500 can offer significant performance at lower costs, it’s important to weigh these options against more specialized solutions like the Raspberry Pi 5 and Intel N100.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which System Is Better for Gaming Applications?
For gaming applications, consider performance benchmarks and gaming peripherals. Choose the Raspberry Pi 5 for efficiency, especially in emulation. If raw power matters more, the Intel N100 might be your better option despite higher energy consumption.
Can Raspberry Pi 5 Support Windows Operating System?
Yes, you can install Windows on a Raspberry Pi 5. However, you’ll need to guarantee Raspberry Pi compatibility and follow the installation process carefully. Expect challenges like driver issues and hardware limitations along the way.
What Are the Best Use Cases for Each Device?
You’ve got the power of innovation at your fingertips! The best applications for Raspberry Pi 5 include lightweight computing and kiosks, while Intel N100 shines in multitasking and productivity, boasting impressive hardware compatibility for diverse needs.
How Does Development Community Support Compare?
When comparing development community support, you’ll find Raspberry Pi 5 relies heavily on community resources and developer forums, while Intel N100 boasts more extensive documentation and established tools, facilitating a smoother development experience.
Is the Intel N100 Upgradeable or Customizable?
The Intel N100 has no upgrade options for the CPU, limiting customization. You can adjust RAM and storage, but overall, its architecture restricts significant enhancements, which may impact your innovation needs.
Conclusion
In the showdown between the Raspberry Pi 5 and Intel N100, it’s clear that each shines in its own arena. The Pi, like a nimble dancer, excels in versatility and efficiency, while the N100 stands tall as a powerhouse for demanding tasks. Ultimately, your choice hinges on what you need: the sleek agility of the Raspberry Pi or the robust strength of Intel. Consider your specific use cases, and select the tool that best fits your creative vision.

I am a retired software engineer with experience in a multitude of areas including managing AWS and VMWare development environments. I bought a relative a mini-PC a year ago and have become passionate about the technology and its potential to change how we deploy software.